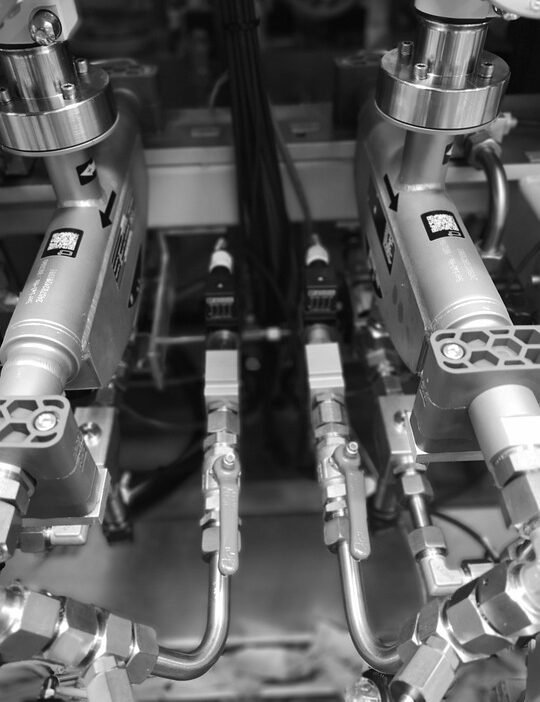
In an increasingly connected world, automation has emerged as a pivotal technology that shapes industries, enhances productivity, and redefines the way we work. Understanding the fundamentals of automation can empower you to harness its potential, whether you’re a business leader, a technology enthusiast, or just someone curious about the future of work.
What is Automation?
At its core, automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It encompasses a broad spectrum of applications, from simple processes like scheduling routine tasks to complex systems that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to optimize workflows.
Types of Automation
-
Fixed or Hard Automation: This type of automation is used in high-volume production settings. It involves specialized equipment designed to automate a specific task, such as assembly line machinery in manufacturing.
-
Programmable Automation: Often found in batch production, programmable automation allows for the reconfiguration of machines to accommodate different tasks. It’s commonly used in scenarios where production volume is moderate, and products change often.
-
Flexible or Soft Automation: Utilized in more dynamic environments, flexible automation systems can adapt to changes rapidly. Robotics and AI play a significant role here, allowing for automation that can adjust to different tasks easily.
-
Industrial Automation: Referring specifically to manufacturing processes, industrial automation optimizes production lines through robotics, sensors, and control systems to boost efficiency and quality.
- Office or Administrative Automation: This applies to the management of office tasks, especially those that are repetitive. Tools like automated email responses, scheduling assistants, and document processing software fall under this category.
Key Technologies Driving Automation
-
Robotics: Robots are increasingly used not just in manufacturing but also in fields like healthcare, logistics, and agriculture. They can perform simple tasks iteratively or handle complex operations requiring precision.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI is revolutionizing how we automate by enabling systems to learn from data and improve over time. Tasks that once required human intelligence, such as data analysis or customer service interactions, are increasingly being automated through chatbots and smart algorithms.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Devices connected to the internet can communicate with one another, creating opportunities for automation in various sectors, from smart homes to industrial applications.
Benefits of Automation
-
Enhanced Efficiency: Automation minimizes human error and reduces time spent on repetitive tasks, leading to increased productivity.
-
Cost Savings: By streamlining operations, businesses can save money in labor costs and reduce the potential for costly mistakes.
-
Scalability: Automation makes it easier to scale operations, as processes can be adjusted and duplicated with minimal input.
-
Improved Quality: Machines can consistently produce outputs to a high standard, reducing variability in quality.
- Employee Satisfaction: By automating mundane tasks, employees can focus on more creative and strategic aspects of their jobs, fostering higher job satisfaction.
Challenges of Automation
Despite its benefits, automation is not without challenges. Job displacement is a significant concern, as many manual jobs may become obsolete. Moreover, the initial cost of implementing automation technologies can be substantial, posing a barrier for smaller businesses. There are also ethical considerations surrounding data security and privacy, especially as automated systems collect and analyze vast amounts of personal data.
The Future of Automation
As technology continues to advance, the landscape of automation will evolve. Trends such as hyper-automation (the combination of automation tools) and autonomous systems (machines that operate independently) are gaining traction. Industries worldwide are exploring how to implement these solutions effectively to drive growth, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of automation is essential in today’s technology-driven world. As we delve deeper into the realm of automation, embracing its challenges and opportunities will empower individuals and organizations to remain competitive. By investing in education and adaptation, we can harness the power of automation to not just simplify tasks but to innovate and inspire the way we live and work. As we look ahead, the question may not be whether we should automate, but how best to do so for a prosperous future.